Type Of Anesthesia
Processing Time
Discharge Time
Activity Start
Varicocele
What is Varicocele?
Varicocele is defined as the abnormal enlargement and twisting of veins that carry dirty blood away from the testicles. This condition usually begins in young age and can progress over time. Initially, varicocele may not present symptoms, but as it progresses, it can cause swelling in the scrotum, pain (particularly in the groin or inner thigh), and abnormalities in sperm count and motility. The treatability of varicocele makes it a significant cause of male infertility. Treatment typically involves surgical intervention aimed at regulating blood flow and improving testicular function.
How Common is Varicocele?
Varicocele is one of the most common andrological problems in men, often appearing during adolescence. Approximately 15% of adolescent males may have varicocele. In adult men after puberty, this rate decreases to about 10%, but the prevalence is higher in males of reproductive age compared to the general population.
Varicocele is typically observed on the left side and rarely on the right side or both sides. This is due to the longer and more vertical venous drainage of the left testicle, which can complicate blood return.
Although varicocele is common in young males, symptoms are often mild and may go unnoticed. However, with advancing age and progression of the condition, symptoms such as swelling in the scrotum, pain, and changes in sperm parameters may become more apparent.
The Connection Between Varicocele and Infertility
The link between varicocele and infertility stems from its potential to negatively affect sperm production and quality. Varicocele is characterized by the expansion and abnormal blood flow in the veins surrounding the testicles. This condition can disrupt the normal temperature regulation of the testicles and damage testicular tissue.
Varicocele can increase the temperature in the testicles, adversely affecting the spermatogenesis process. Elevated temperatures can hinder or disrupt the normal development of sperm. Additionally, abnormal blood flow caused by varicocele can affect the nourishment and oxygen supply to the testicles, further impeding healthy sperm development.
In terms of infertility, varicocele can lead to reduced sperm count, impaired sperm motility, and morphological abnormalities. These issues can reduce the chances of natural conception. In men with varicocele, treatment may improve sperm parameters and increase the likelihood of natural pregnancy.
Therefore, men diagnosed with varicocele should consider evaluating surgical or other treatment options to improve reproductive health. Treatment is determined based on the size of the varicocele, symptoms, and its impact on the patient’s reproductive health.
Symptoms of Varicocele
Varicocele often presents with no symptoms or mild symptoms initially. Symptoms can progress over time or become more pronounced.
- Swelling in the Scrotum: The most common symptom is swelling or varicosity in one or both sides of the scrotum. A noticeable network of veins may be visible in the scrotum.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some men may experience pain or discomfort in the scrotum. Typically, the pain can be mild or may radiate to the groin, lower back, or inner thighs intermittently.
- Sensitivity in Testicles: Some men with varicocele may experience sensitivity or a feeling of heaviness in the testicles. This is often more noticeable at the end of the day or after standing for prolonged periods.
- Changes in Sperm Parameters: Varicocele can negatively affect sperm production and quality. This may be reflected in sperm analysis with reduced sperm count, decreased motility, or abnormal sperm morphology.
- Visible Vein Network: In men with varicocele, a prominent network of veins may be observed on or beneath the scrotum. These veins are typically located within the pouch that surrounds the testicles.
How is Varicocele Diagnosed?
Varicocele diagnosis is typically made through physical examination. During the examination, enlarged and twisted veins may be felt in the scrotum and testicles. Diagnosis is often confirmed through this simple physical examination. However, in some cases, physical examination may not be conclusive or may be confused with other conditions. In such cases, Color Doppler Ultrasound may be used. Color Doppler Ultrasound helps visualize blood flow and the enlargement of veins, aiding in confirming the diagnosis of varicocele and determining its severity. This method is particularly useful when physical examination is challenging or a definitive diagnosis is required.
Grading of Varicocele
Varicocele is generally classified into three grades based on visual and physical examination of the enlarged veins. The grading is based on the following criteria:
- Grade 1: Mild varicocele is characterized by small varicose veins felt in the scrotum. At this stage, varicocele is generally not visible and typically does not affect the testicles.
- Grade 2: Moderate varicocele is characterized by visibly enlarged veins in the scrotum. The testicles may be slightly larger, and the patient may experience mild pain or discomfort.
- Grade 3: Severe varicocele is characterized by large, prominent, and twisted varicose veins in the scrotum. The testicles may be larger than normal, with more pronounced pain and discomfort, and significant abnormalities in sperm parameters may be observed.
Varicocelectomy Surgery
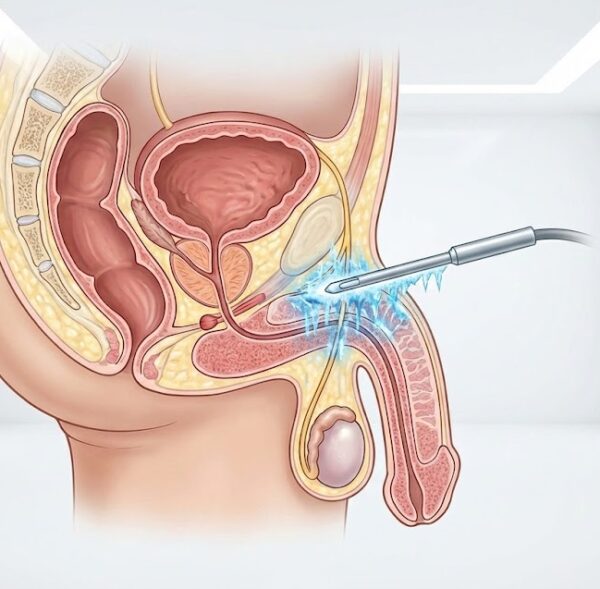
Varicocelectomy is a commonly used surgical procedure for treating varicocele. This surgery is performed to alleviate symptoms caused by varicocele and address infertility issues in men. The surgery is typically performed using microsurgical techniques under local or general anesthesia.
During the surgery, a small incision is made in the lower part of the scrotum to locate and either tie off or cut the enlarged veins. This procedure aims to regulate blood circulation around the testicles and reduce the effects caused by varicocele. Varicocelectomy generally reduces pain, corrects testicular enlargement, and improves sperm quality.
The recovery process after surgery is usually quick, with return to normal daily activities within a few days. However, full recovery and improvement in sperm parameters may take several weeks. Post-operative complications are rare, but risks such as infection or bleeding, as with any surgical procedure, are present.
Varicocelectomy can be an effective option for relieving varicocele symptoms and correcting its negative effects on fertility. However, careful evaluation and consideration of the patient’s health condition are important before surgery.