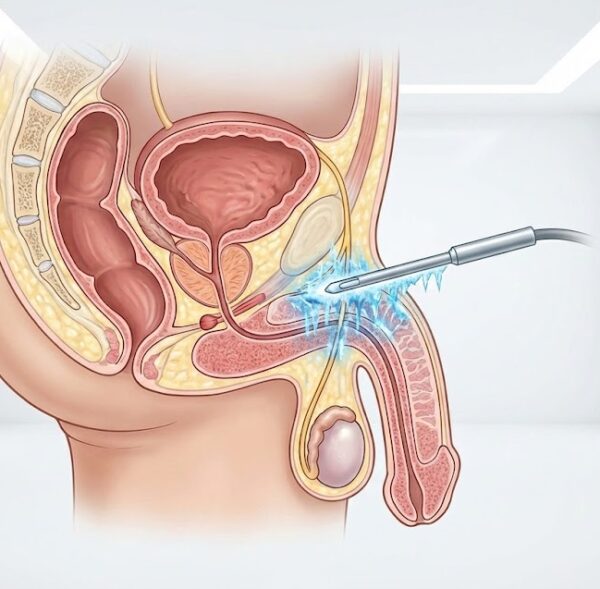
Type Of Anesthesia
Processing Time
Discharge Time
Activity Start

HPV / Wart Combine Treatments
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection is a viral disease that can cause warts (condylomas) in the genital area of both women and men. These warts usually have a cauliflower appearance, can vary in size, and are generally painless. Genital warts affect over 1% of the population and are most commonly seen between the ages of 20-30. In recent years, the incidence of genital warts in Turkey has also increased. Genital warts detected in men are extremely important for public health and need to be treated.
Incubation Period
The incubation period refers to the time interval between exposure to the virus and the appearance of disease symptoms. This period, which varies depending on the virus and the individual, can sometimes manifest immediately after exposure or months or even years later. For viruses like HPV, the incubation period generally ranges from 1 to 6 months. However, in some cases, the virus can remain in the body without showing symptoms for a long time. Therefore, accurately assessing the incubation period is crucial for understanding the spread and control of viruses.
How is it Transmitted?
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is a virus that is primarily transmitted through sexual contact. The most common transmission route is sexual intercourse; however, the risk of HPV transmission is also associated with other forms of sexual contact, including oral sex, anal sex, and genital contact. The virus can pass from an infected person to a healthy person after contact with skin or mucous membranes. The use of condoms can reduce the risk of HPV transmission but does not completely eliminate it. Additionally, in rare cases, HPV can be transmitted from mother to baby during childbirth, leading to genital warts in infants.
HPV Types in Men
There are different types of HPV in men, and they are generally sexually transmitted viruses. More than 70 types of HPV have been identified, with approximately 30 affecting the ano-genital region. The majority of genital warts in men (80-90%) are typically associated with HPV types 6 and 11. These types generally do not exhibit carcinogenic properties, but carcinogenic potential HPV subtypes (e.g., types 16 and 18) can be found in asymptomatic lesions.
Genital warts in men are usually 2-10 mm in diameter and are commonly seen on the foreskin (prepuce), frenulum (sensitive area just below the head of the penis), mons pubis, coronal sulcus (the groove at the head of the penis), scrotum (sack surrounding the testicles), groin, and around the anus. Rarely, they can also be seen in areas such as the urethra (urinary tract) and bladder.
The appearance of genital warts is often described by patients as bumps or lesions. They have a cauliflower-like appearance and possess a flexible and soft texture.
Genital Wart Treatment
The treatment of genital warts aims to control the skin lesions caused by the HPV virus in infected individuals. Treatment options are usually determined based on the number, size, prevalence, and location of the warts. The most commonly used treatment methods include topical medications. Chemical substances like podophyllin and podophyllotoxin can halt and reduce the growth of warts when applied locally. Another topical treatment option is imiquimod cream, which helps the body eliminate warts by stimulating the immune response. Invasive procedures such as freezing the warts (cryotherapy), surgical removal, or laser ablation may also be required, especially for large or resistant warts. Each patient’s treatment plan is personalized and determined by the doctor, so it is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate treatment method. Additionally, during the treatment process, it is crucial to inform sexual partners and use protection methods, as HPV is a sexually transmitted virus and can recur.
Are Condoms Protective Against the Virus?
Yes, condoms have a protective effect against sexually transmitted viruses like HPV (Human Papillomavirus). Viruses like HPV can be transmitted from person to person during sexual contact. Condoms can reduce the risk of infection by preventing the virus from entering the body during sexual intercourse. However, the risk of HPV transmission is not limited to genital contact; they can be transmitted from any area of contact. Therefore, using condoms plays a significant role in preventing the spread of viruses like HPV, but it does not provide complete protection. Additionally, condoms can also protect against other sexually transmitted infections, so their regular and correct use is recommended.